In this post, I'm sharing interview questions on Mongo DB replication and configuration.
Question 1:
Why we need replication in Mongo DB?
Answer:
Mongo DB replication has two benefits:
- If one database node is down, we can get data from other nodes.
- Replication can also be done for the purpose of load balancing.
Question 2:
How to setup replication in Mongo DB?
Answer:
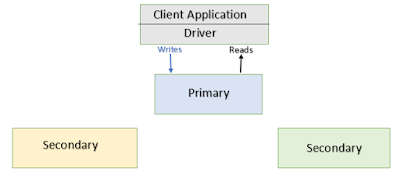
In Mongo db , replication process can be setup by creating a replica set. In Mongo db, a replica set contains multiple Mongo db servers. In this group of Mongo db servers, one server is known as a primary server and others are known as secondary servers.
Every secondary server always keeps copies of the primary's data. So, if anytime the primary server goes down, then the new primary server is selected from the existing secondary servers and process goes on.
The replication process works as below with the help of a replica set:
Replica set is a group of one or more standalone mongo db servers [Normally, 3 Mongo db servers are required].
In a replica set, one server is marked as primary server and rest are marked as secondary server.
Data writes into the primary server from the application first. Then all the data replicates to the secondary servers from the primary server.
When the primary server is unavailable due to hardware failure or maintenance work, the election process starts to identify the new primary server and select a primary server from the secondary lists.
When the failed server recovered, it will again join the replica set as a secondary server.
Question 3:
How to configure replication in Mongo DB?
Answer:
I will tell here , how to convert a standalone Mongo db instance into a replica set. This process is not an ideal process for the production environment. Because in production environment, if we need to establish a replica set, then we need to provide three different Mongo db instances for the replica set.
Step 1:
Start a mongo shell with the --nodb options from the command prompt. It will start a shell without any connection with the existing mongodb instance.
Command is : mongo --nodb
Step 2:
Now, create a replica set with the below commands:
replicaSet = new ReplSetTest({name:'rsTest', nodes : 3})
This command instructs the shell to create a replica set with three node servers: one primary and two secondaries.
Step 3:
Now run the below commands one by one to start the mongo db server instances:
1. replicaSet.startSet() - This command starts the three mongo db processes.
2. replicaSet.initiate() - This command configures the replication.
Now, we have three mongo db processes locally on ports port1, port2, port3 [These will be integer values].
Step 4:
Now open another command prompt and connect the mongo db running on port port1.
1. conn1 = new Mongo("localhost:port1");
2. connection to localhost:port1
3. rsTest : PRIMARY>
Note that, when we connect a replica set member, the prompt changes to rsTest: PRIMARY. Here PRIMARY is the state of the member and rsTest is the identifier of the replica set.
Question 4:
How to change replication configuration?
Answer:
After defining a replica set, we can change the replica set at any time. We can add new members , remove any existing members.
There is a mongo shell helper method is available to add new replica set members or remove existing replica set members.
To add a new member into the replica set, we need to run the below command:
rs.add("server-4: 20005")
Similarly, we can remove any members from the existing replica set using the below command:
rs.remove("server-2:20002")
If we need to check the existing configuration of the replication, then we need to run the below command in the shell:
rs.config()
Question 5:
How does syncing work in Mongo DB?
Answer:
The main objective of the replication process is to keep the same or an identical set of data on multiple servers. For performing this task, MongoDB always maintains a log of operations or oplog which contains every write information into the primary server. This log is a collection that exists in the local database on the primary server.
The secondary servers are queries of this collection for obtaining the operation details so that they can replicate that data.
Every secondary server maintains it's own oplog where Mongo db captures each operation related to the replication process from the primary server.These log files allow any replica set members to use as a sync source for other members.
The secondary server always first fetches the information related to the pending operations from the primary members, then apply that operation to their own data set and then writes down the logs about that operation into the oplog.
That's all for this post.
Thanks for reading!!



No comments:
Post a Comment