Hi friends,
In this post, I'm sharing Techincal architect interview questions-answers asked in Incedo.
You can also go through other interviews posts here:
Question 1:
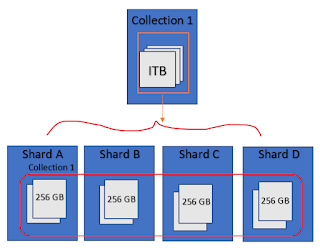
What is database sharding? Why we need database sharding?
Answer:
Question 2:
What are the types of database sharding?
Answer:
Example of Vertical partitioning:
fetch_user_data(user_id) -> db["USER"].fetch(user_id)
fetch_photo(photo_id) -> db["PHOTO"].fetch(photo_id)
Example of Horizontal partitioning:
fetch_user_data(user_id) -> user_db[user_id % 2].fetch(user_id)
Question 3:
How to implement sharding in MongoDB?
Answer:
When deploying sharding, we need to choose a key from a collection and split the data using the key's value.
Task that the key performs:
Question 4:
What is the use of Amazon EC2? What are the steps to deploy on EC2?
Answer:
Amazon EC2 : Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud
It offers ability to run applications on the public cloud.
It eliminates investment for hardware. There is no need to maintain the hardware. We can use EC2 to launch as many virtual servers as we need.
Steps to deploy on EC2:
· Launch an EC2 instance and SSH into it. Note: This instance needs to be created first on AWS console[console.aws.amazon.com]. And we should also have certificate to connect to EC2 instance.
· Install Node on EC2 instance, if our app is in Angular.
· Copy paste code on EC2 instance and install dependencies.
· Start server to run.
Question 5:
How will we use Amazon S3?
Answer:
For using S3, we need to first choose S3 from AWS console and then we need to create a bucket in that for storing our files.
After creating the bucket, we need to click on the upload option and select jar file or any file from our computer and upload it to S3.
While uploading file to S3, we need to provide it some access level so that we can download it from S3 to EC2 instance.
So before that we need to make EC2 instance up and running.
And then we need to connect from local to EC2 instance using private key that we have. For connecting to EC2, we need to do SSH login [from terminal] using some certificate and using some SSH command.
Now we need to install java on EC2 [As , it is not there by default]. After that we can download our jar file from S3 to EC2 instance.
Now just run this jar using java -jar <filename> to run the springboot application.
Question 6:
What are the best Code Review Practices?
Answer:
Question 7:
What are the types of Http Error codes?
Answer:
There are 5 types of Error codes:
1XX Informational:
100: Continue
2XX Success:
200 : OK
201 : Created
202 : Accepted
204 : No Content
3XX Redirection:
4XX Client Error:
400 : Bad Request
401 : Unauthorized
402 : Payment Required
403 : Forbidden
404 : Not Found
5XX Server Error:
500 : Internal Server Error
501 : Not Implemented
502 : Bad Gateway
503 : Service Unavailable [Website's server is simply not available]
Question 8:
What are the Asymptotic Notations?
Answer:
To calculate running time complexity of an algorithm, we use following asymptotic notations:
Big Oh Notation O:
The notation O(n) is the formal way to express the upper bound of an algorithm's running time.
It measures the worst case time complexity or the longest amount of time an algorithm can possibly take to complete.
For example, for a function f(n)
O(f(n)) = { g(n) : there exists c > 0 and n0 such that f(n) <= c.g(n) for all n > n0. }
Omega Notation:
The Omega notation is the formal way to express the lower bound of an algorithm's running time. It measures the best case time complexity or the best amount of time an algorithm can possibly take to complete.
For example, for a function f(n)
Theta Notation:
In this post, I'm sharing Techincal architect interview questions-answers asked in Incedo.
You can also go through other interviews posts here:
- https://javaroidinterview.blogspot.com/
- Incedo Interview on SQL knowledge
- SQL based interview-1
- Java Interview @ OLX
- Java Interview @ Gemini Solutions
- Java Interview @ SAP
- Java Interview @ Rocketalk
- Java Interview @ Aricent
- Java Interview @ WDTS
Question 1:
What is database sharding? Why we need database sharding?
Answer:
Sharding involves breaking up one's data into two or more
smaller chunks, called logical shards. The logical shards are then distributed
across separate database nodes, referred to as physical
shards, which can hold multiple logical shards.
Sharding is a method of splitting and storing a single logical dataset
in multiple databases.
Sharding adds more servers
to a database and automatically balances data and load across various servers.
These databases are called shards.
Sharding
is also referred as horizontal partitioning. The distinction of horizontal vs vertical comes
from the traditional tabular view of a database.
What are the types of database sharding?
A database can be split
vertically — storing different tables & columns in a separate database, or
horizontally — storing rows of a same table in multiple database nodes.
Example of Vertical partitioning:
fetch_user_data(user_id) -> db["USER"].fetch(user_id)
fetch_photo(photo_id) -> db["PHOTO"].fetch(photo_id)
Example of Horizontal partitioning:
fetch_user_data(user_id) -> user_db[user_id % 2].fetch(user_id)
Vertical
sharding is implemented at application level – A piece of code routing reads
and writes to a designated database.
Natively
sharded DB’s are : Cassandra, MongoDB
Non-sharded
DB’s are : Sqlite, Memcached etc.
When we need to do sharding?
Answer:
·
When
the data set outgrows the storage capacity of a single MongoDB instance.
·
When
a single MongoDB instance is unable to manage write operations.
Question 3:
How to implement sharding in MongoDB?
Answer:
When deploying sharding, we need to choose a key from a collection and split the data using the key's value.
Task that the key performs:
- Determines document distribution among the different shards in a cluster.
Choosing the correct shard key:
To enhance
and optimize the performance, functioning and capability of the DB, we need to
choose the correct shard key.
Choosing correct shard key depends on
two factors:
- The
schema of the data
- The
way database applications query and perform write operations.
Using range-based Shard key:
In range-based sharding, MongoDB divides data sets into different ranges based on the values of shard keys. In range-based sharding, documents having "close" shard key values reside in the same chunk and shard.
Data
distribution in range-based partitioning can be uneven, which may negate some
benefits of sharding.
For example,
if a shard key field size increases linearly, such as time, then all requests
for a given time range will map to the same chunk and shard. In such cases, a
small set of shards may receive most of the requests and system would fail to
scale.
Hash-based sharding:
In this ,
MongoDB first calculates the hash of a field’s value and then creates chunks
using those values. In this sharding, collections in a cluster are randomly
distributed.
No
real schema is enforced:
- We
can have different fields in every document if we want to.
- No
single key as in other databases:
o
But
we can create indices on any fields we want, or even combinations of fields.
o
If
we want to shard, then we must do so on some index.
Question 4:
What is the use of Amazon EC2? What are the steps to deploy on EC2?
Answer:
Amazon EC2 : Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud
It offers ability to run applications on the public cloud.
It eliminates investment for hardware. There is no need to maintain the hardware. We can use EC2 to launch as many virtual servers as we need.
Steps to deploy on EC2:
· Launch an EC2 instance and SSH into it. Note: This instance needs to be created first on AWS console[console.aws.amazon.com]. And we should also have certificate to connect to EC2 instance.
· Install Node on EC2 instance, if our app is in Angular.
· Copy paste code on EC2 instance and install dependencies.
· Start server to run.
OR:
- Build
out Spring boot app in our own computer. Make .jar file.
- Upload
this .jar on S3
- Create
EC2 instance.
- SSH
into it from our computer.
- Now,
we are in EC2 instance.
- We
can install JDK now.
- And
using java - .jar file path, we can run our application.
Question 5:
How will we use Amazon S3?
Answer:
For using S3, we need to first choose S3 from AWS console and then we need to create a bucket in that for storing our files.
After creating the bucket, we need to click on the upload option and select jar file or any file from our computer and upload it to S3.
While uploading file to S3, we need to provide it some access level so that we can download it from S3 to EC2 instance.
So before that we need to make EC2 instance up and running.
And then we need to connect from local to EC2 instance using private key that we have. For connecting to EC2, we need to do SSH login [from terminal] using some certificate and using some SSH command.
Now we need to install java on EC2 [As , it is not there by default]. After that we can download our jar file from S3 to EC2 instance.
Now just run this jar using java -jar <filename> to run the springboot application.
Question 6:
What are the best Code Review Practices?
Answer:
Clean Code
·
Use
intention-revealing names
·
Use
Solution-Problem domain names
·
Classes
should be small
·
Functions
should be small
·
Functions
should do one thing
·
Don’t
repeat yourself(Avoid duplication)
·
Explain
yourself in code : Comments
·
Use
Exceptions rather than return codes
·
Don’t
return Null
Security
·
Make
class final if not being used for inheritance
·
Avoid
duplication of code
·
Minimize
the accessibility of classes and members
·
Document
security related information
·
Input
into a system should be checked for valid data size and range
·
Release
resources (Streams, Connections) in all cases
·
Purge
sensitive information from exceptions
·
Don’t
log highly sensitive information
·
Avoid
dynamic SQL, use prepared statement
·
Limit
the accessibility of packages, classes, interfaces, methods and fields
·
Avoid
exposing constructors of sensitive classes
·
Avoid
serialization of sensitive classes
·
Only
use JNI when necessary
Performance
·
Avoid
excessive synchronization
·
Keep
synchronized sections small
·
Beware
the performance of String concatenations
·
Avoid
creating unnecessary objects
General
·
Don’t
ignore exceptions
·
Return
empty arrays or collections , not nulls
·
In
public classes, use accessor methods not public fields
·
Avoid
finalizers
·
Refer
to objects by their interfaces
·
Always
override toString()
·
Document
thread safety
·
Use
marker interfaces to define types
Static Code Analysis
·
Check
static code analyzer report for the classes added/modified
Question 7:
What are the types of Http Error codes?
Answer:
There are 5 types of Error codes:
1XX Informational:
100: Continue
2XX Success:
200 : OK
201 : Created
202 : Accepted
204 : No Content
3XX Redirection:
4XX Client Error:
400 : Bad Request
401 : Unauthorized
402 : Payment Required
403 : Forbidden
404 : Not Found
5XX Server Error:
500 : Internal Server Error
501 : Not Implemented
502 : Bad Gateway
503 : Service Unavailable [Website's server is simply not available]
Question 8:
What are the Asymptotic Notations?
Answer:
To calculate running time complexity of an algorithm, we use following asymptotic notations:
Big Oh Notation O:
The notation O(n) is the formal way to express the upper bound of an algorithm's running time.
It measures the worst case time complexity or the longest amount of time an algorithm can possibly take to complete.
For example, for a function f(n)
O(f(n)) = { g(n) : there exists c > 0 and n0 such that f(n) <= c.g(n) for all n > n0. }
Omega Notation:
The Omega notation is the formal way to express the lower bound of an algorithm's running time. It measures the best case time complexity or the best amount of time an algorithm can possibly take to complete.
For example, for a function f(n)
Theta Notation:
The notation theta (n) is the formal way to express both the lower bound and upper bound of an algorithm's running time.It is represented as follows:










No comments:
Post a Comment